TB Testing Clinic in Norman (HealthPlex), OK
Tuberculosis (TB) is a potentially fatal and highly infectious bacterial illness that mostly impacts the lungs but can also damage the kidneys, spine, and brain. It spreads through coughing or sneezing from an infected person. Get a professional medical evaluation at Immediate Care of Oklahoma if you are anxious about symptoms that might indicate tuberculosis. Dr. Kevin Penwell, D.O., can assist in making a diagnosis and creating a customized treatment plan for your condition. For more information, contact us or schedule an appointment online. We are conveniently located at 3321 W. Tecumseh Rd. 125, Norman, OK 73072.


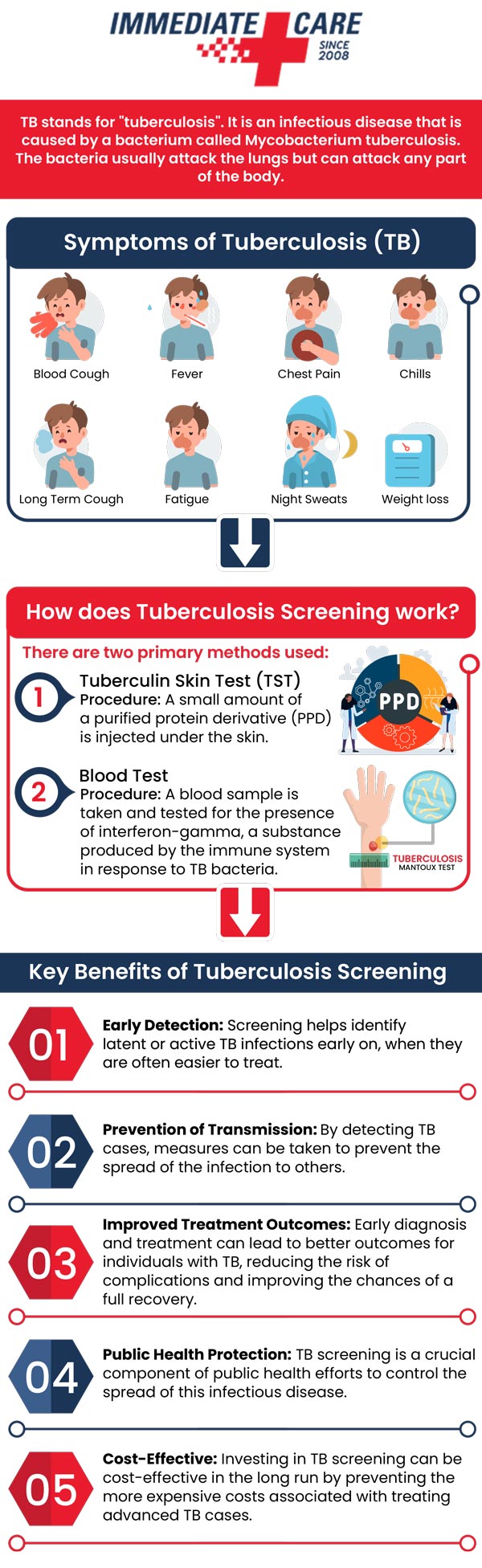
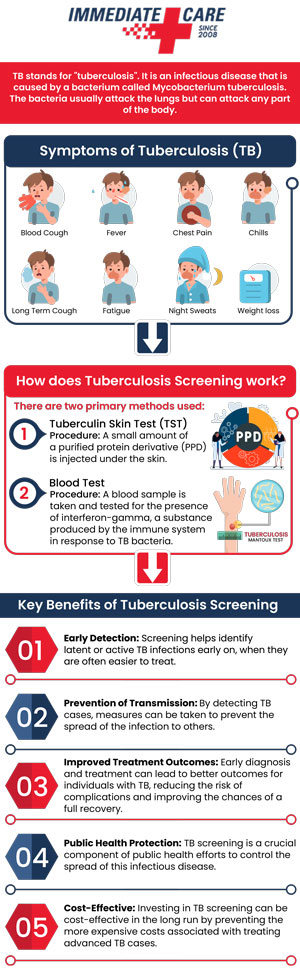
Table of Contents:
How is TB caused?
When should you get tested for TB?
What tests are done to confirm TB?
How long does the TB test take?
TB, commonly known as tuberculosis, is a communicable disease that is caused by a bacterium known as Mycobacterium tuberculosis. This bacterium can spread from one person to another through small droplets released into the air via coughing, sneezing, or even speaking. When an individual inhales these droplets, the bacteria enter their lungs and begin to multiply.
TB primarily affects the lungs, but it can sometimes spread to other parts of the body, such as the brain, kidneys, and spine. The symptoms of TB include an ongoing cough, chest pain, fatigue, weight loss, fever, and night sweats. If left untreated, TB can cause significant damage to the lungs and many other organs and can even be fatal.
Amazingly enough, TB is a treatable and curable disease. The treatment involves a long-term course of antibiotics that must be taken for several months to completely eradicate the bacteria from the body. It is essential to complete the full course of medication to prevent the development of drug-resistant strains of the bacteria.
You should consider getting tested for TB if you have been in close contact with someone who has been diagnosed with TB, or if you are experiencing symptoms such as an ongoing cough, chest pain, fatigue, weight loss, fever, and night sweats. Additionally, if you have a weakened immune system due to conditions such as HIV/AIDS, diabetes, or cancer, you may be at a higher risk of developing TB and should consider getting tested.
TB tests are usually done in two ways – a skin test or a blood test. The skin test is completed by injecting a minute amount of fluid, called tuberculin, under the skin of the forearm and then checking the site for a reaction after a few days. The blood test, also known as interferon-gamma release assays (IGRAs), checks for the presence of TB antibodies in the blood.
It is important to note that not everyone who is exposed to TB will develop the disease. If you do test positive for TB, further testing will be needed to determine if the infection is active or latent.
Several tests that can be done to confirm tuberculosis (TB). If you have a suspected case of TB, your doctor may need to require a physical exam, discuss your medical history, and order some tests to confirm the diagnosis.
One of the most common tests used to diagnose TB is a sputum test, which involves examining a sample of mucus brought up from the lungs under a microscope. If the TB bacteria are present, they can be seen in the sample. The sputum test may need to be repeated several times to confirm the diagnosis.
Another test that may be used is a chest X-ray, which can help identify signs of TB in the lungs, such as abnormal shadows or areas of inflammation. If the X-ray is suggestive of TB, additional tests such as a sputum culture or a molecular test may be done to confirm the diagnosis.
It is important to note that not all tests for TB are 100% accurate, and a combination of tests may be needed to confirm the diagnosis.
The length of time it takes to get the results of a tuberculosis (TB) test can vary greatly depending upon the type of test that is done.
A skin test, also known as a Mantoux test, is a skin test done by injection under the skin of the forearm and then checking the site for a reaction after 48 to 72 hours. The reaction is then measured in millimeters of the swelling at the injection site. If the swelling is a certain size, the test is considered positive.
Blood tests known as interferon-gamma release assays (IGRAs), check for the presence of TB antibodies in the blood. These tests are usually done in a laboratory, and the results can take several days to several weeks to come back.
In some cases, other tests such as chest X-rays, sputum cultures, or biopsies may be needed to confirm a diagnosis of TB. These tests may take longer to produce results, and your healthcare provider will let you know how long you can expect to wait for the results.
Get tested for tuberculosis from our passionate team of professionals at Immediate Care Of Oklahoma, to make it easier for you to take control of your health and well-being. For more information, contact us or schedule an appointment online. We are conveniently located at 3321 W. Tecumseh Rd. 125, Norman, OK 73072. We serve patients from West Moore OK, Norman (HealthPlex) OK, Norman (24th) OK, Edmond OK, Yukon OK, I-240 & Sooner RD OK, Tecumseh OK, and Bethany OK.


Additional Services You May Need
▸ Urgent Care Services
▸ Illness + Injuries
▸ On Site Lab + X-Ray
▸ Helpful Health
▸ Motor Vehicle Accidents
▸ Drug Testing
▸ MRO
▸ UTI Treatment
▸ Employment Physicals
▸ Workers Comp
▸ Strep Throat Treatment
▸ Pregnancy Testing
▸ Blood Pressure Testing
▸ Urinalysis
▸ Mononucleosis Treatment
▸ Suture Removal
▸ Respiratory Syncytial Virus
▸ OccMed